[ad_1]
‘New report looks at ways to build confidence and increase vaccine uptake’
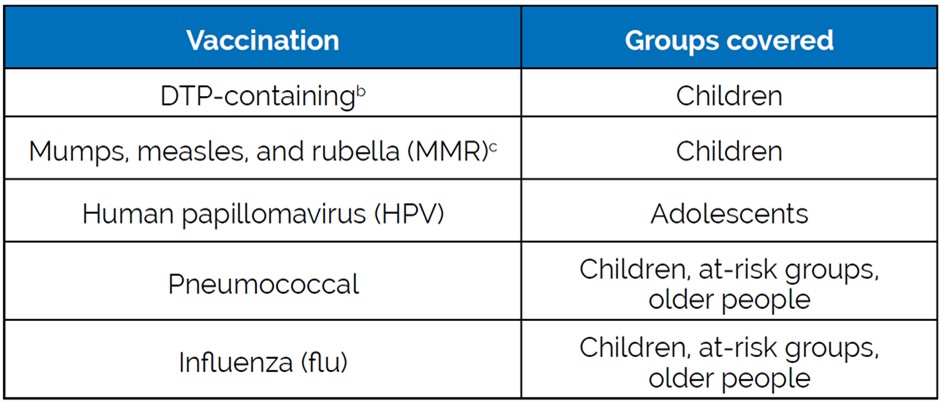
Vaccination coverage in Central and Eastern Europe is lower than in some Western European countries, especially for vaccines that protect adolescents and adults. Low vaccination coverage can occur for a variety of reasons, including affordability, access to vaccination, and low levels of vaccine acceptance. EU data shows low confidence in vaccines in Central and Eastern European countries.
A new report from the International Longevity Center UK (ILC-UK) points to declining trust in the health system, low spending on preventive care and a lack of recommendations for some vaccines.
ILC-UK, a founding member of the ILC European Network and the UK’s leading authority on longevity and demographic change, has published a new report, Shifting the Narrative: Improving Vaccine Uptake in Central and Eastern Europe. The report asks, why are Central and Eastern European countries lagging behind the EU average? And how can we restore trust in governments and health systems to increase vaccination rates across Europe?
Just 21% of EU citizens report having low confidence in their country’s health system, compared to 49% in some parts of Eastern Europe.
The 11 Central and Eastern European countries surveyed in the new ILC report (Bulgaria, Croatia, Czech Republic, Estonia, Hungary, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Romania, Slovakia and Slovenia) have historically had lower health spending than other European countries. It lags behind other countries.
The average healthcare expenditure per EU resident in 2020 was €2,110. Romania had the lowest spending in this part of Central and Eastern Europe, at 713 euros.
If rollout is delayed, it is easy to see how vaccination will be deprioritized among many other demands on health budgets. Health interventions will not occur without effective awareness campaigns and the health system infrastructure to enable them.
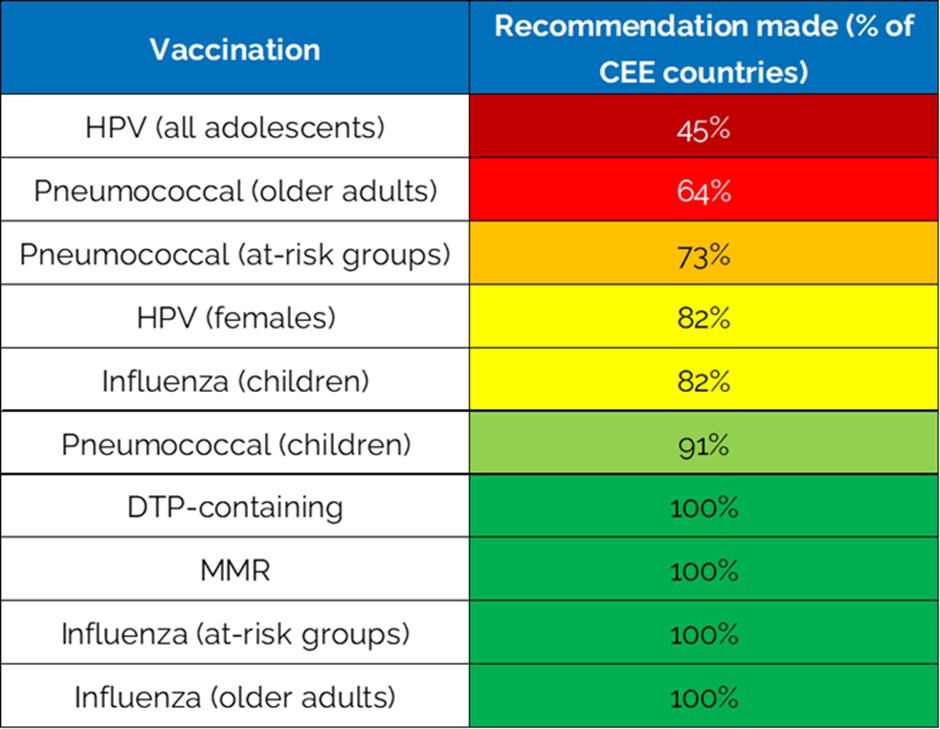
The report determined that the following factors together explain why vaccine rollout has been slower in Central and Eastern Europe than in the rest of the EU.
unreliable: Lack of commitment from politicians and disorganized responses to COVID-19 in several countries have led to a breakdown in confidence in vaccinations and a decline in public confidence.
historical determinants: Distrust of authorities often stems from previous forms of government and politics that restricted individual freedom.
lack of communication: Vaccination communication is often too slow, influenced by anti-vaccine rhetoric, and too often unchecked.
Inaccessible medical services: Inadequate access to vaccination and scarce funding suggest to some that vaccination is not a priority for governments and therefore individuals do not need to prioritize vaccination.
lack of health education: Low awareness and lack of engagement means that many people in the region are not prioritizing vaccination.
The interventions needed to address this disparity in vaccine uptake are wide-ranging and relate to all aspects of healthcare. The report recommends action at national and EU level and advocates an approach to increasing intake across society.
Health leaders, clinicians, faith leaders, community leaders, pharmacists, and many other stakeholders have a role to play in normalizing vaccination and helping others understand its importance.
Main recommendations
- Invest in systems designed for prevention. Patients, healthcare professionals, and policy makers need seamless access to the right information to support improved vaccine access and uptake.
- Take action to inspire and engage. The benefits of vaccination should be clearly communicated and there should be consistent communication at all levels of society.
- Democratizing access to prevention: Infrastructure at each level of the health system must facilitate preventive interventions. This is part of an overall effort to ensure that health outcomes do not vary by wealth.
- Supports effective use of technology. Digital communication tools should be used to reach underserved groups and counter anti-vaccination narratives that are too accessible online.
To read the full report and its recommendations, click here
For more information on ILC adult immunizations, click here
Related article
Bridging the gap: A data-driven vision for life course immunizationNovember 10, 2023
Inform and protect: Transmit knowledge, not disease.September 18, 2023
[ad_2]
Source link