[ad_1]
The current El Niño weather pattern is currently “historically strong,” federal scientists announced. They also predict that a comparable La Niña event will occur later this year.
Both weather patterns dramatically affect weather and climate in the United States and around the world. The typical winter effect of a strong El Niño is storms across the southern United States from California to Florida.
A strong El Niño, colloquially known as “Super El Niño,” and climate change warmth will also contribute to rising global temperatures in 2023, making that year the warmest since accurate weather records began in the late 1800s. Ta.
El Nino’s impact on the US continues until April
El Niño will weaken as the transition to La Niña occurs, but its impact on U.S. weather is expected to continue into April, the Climate Prediction Center said in a statement Thursday. This typically brings additional storms to the southern tier of the United States, from California to Florida. This also means that temperatures are above average in many areas of the northern tier of the United States.
El Niño may also increase the likelihood of above-normal tornado activity in south-central Florida in the coming months.
Overall, El Niño’s impact on the United States is most pronounced from late fall through spring, NOAA said.

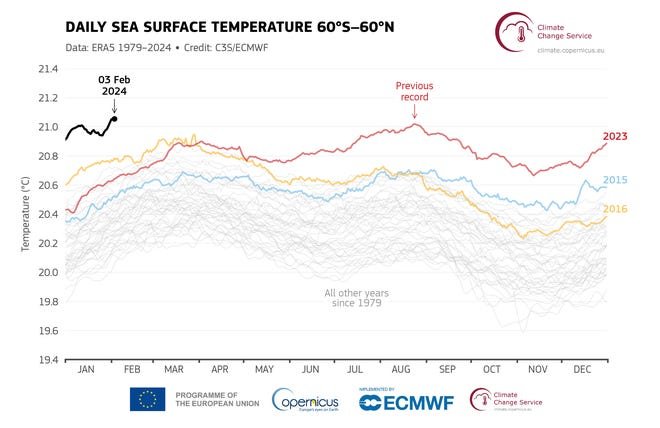
Record warmth in January
Global climate data has begun to be collected for January, which saw back-to-back warmest months on record. According to the Copernicus Climate Change Service, “January 2024 was the warmest January on record globally.”
“This is the eighth consecutive month and the hottest day on record for each month,” the service added in a statement.
Data from NASA January also marked record-warm temperatures around the world.

Does La Niña mean more hurricanes?
And it’s worrisome because when La Niña events occur later in the year, the pattern often increases hurricane activity in the Atlantic Ocean. Colorado State University meteorologist Phil Klotzbach Posted on X Thursday.
However, Klotzbach said, “It’s only February, and a lot can change between now and when Atlantic hurricane season is in full swing, usually in early to mid-August.” It should be noted that there are,” he added.
AccuWeather meteorologist Brian Rada said a La Niña event “could have a significant impact on the U.S. weather forecast for next winter.” “Generally, the south will have a dry, mild winter, the northeast will experience colder conditions, and the northwest will experience more frequent storms, but it is still too early to tell what next winter will bring.”
What is El Niño?
El Niño is a natural climate pattern in which sea surface temperatures in the central and eastern tropical Pacific Ocean are warmer than average. Occurs on average every 2 to 7 years.
The name means “little boy” or “Christ child” in Spanish. El Niño was originally recognized by fishermen off the coast of South America in the 1600s when unusually warm water appeared in the Pacific Ocean around Christmas.
The entire natural climate cycle is officially known as El Niño (Southern Oscillation), and scientists refer to it as ENSO. This cycle moves back and forth between warm and cold ocean water in areas along the equator of the tropical Pacific Ocean. La Niña is characterized by lower than average seawater levels in the region.
[ad_2]
Source link