[ad_1]
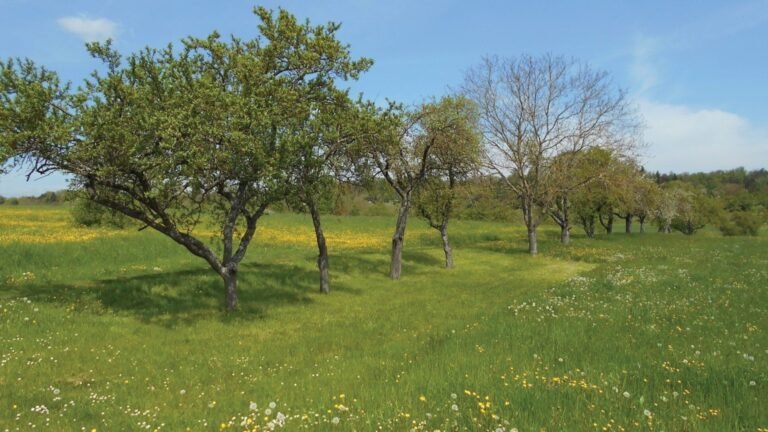
An orchard in Rutesheim-Peruz, southern Germany. Credit: Klaus Henle. CC-BY4.0
× close
An orchard in Rutesheim-Peruz, southern Germany. Credit: Klaus Henle. CC-BY4.0
The study, led by researchers from the Helmholtz Center for Environmental Research and Macquarie University, highlights the important ecological role of traditional orchard meadows and suggests ways to protect these landscapes. It seeks political and public support and encouragement for farmers.
Paper published in nature conservationreviews the effects of management, habitat, and landscape characteristics on the biodiversity of orchard pastures in Central Europe.
The orchard meadow is characterized by a combination of cultivated grassland and scattered fruit trees, exhibiting high flora and fauna biodiversity. Despite their ecological value, these habitats have been in decline since the mid-19th century due to declining economic value. They currently face threats from land abandonment and agricultural intensification.
This study highlights the importance of appropriate management intensity, connectivity with neighboring habitats, and preservation of structural diversity to maintain and enhance the conservation value of orchard meadows.
The findings also advocate a nuanced understanding of management implications for the entire taxon and point out the limitations of available research on orchard pastures in Central Europe.
Currently the definition is loose, but the research team advocated for a clear definition of orchard meadows in order to create a common term in Europe and make their assessment and protection easier.
They suggest that orchard pastures should be listed in the Council of the European Union’s Habitats Directive and farmers should receive incentives for their maintenance. Finally, the research team calls for political and public support to prevent the loss and abandonment of these biodiverse landscapes.
Schematic diagram showing the impact of enhanced management on species richness. Credit: Sattler et al. CC-BY4.0
× close
Schematic diagram showing the impact of enhanced management on species richness. Credit: Sattler et al. CC-BY4.0
“One of the ways the public can help protect these habitats is through consumer behavior, specifically purchasing local products from orchard meadows. It is important to subsidize products and prioritize them in local markets,” said lead author Cornelia Sattler.
“As long as fruit from orchard meadows is treated as a ‘by-product’ in the market, it will be difficult to persuade people to buy local products. “It is necessary to bridge the economic gap between orchards and pastures,” she concluded.
For more information:
Cornelia Sattler et al., Effects of management, habitat, and landscape characteristics on the biodiversity of orchard-meadows in Central Europe: A brief review; nature conservation (2024). DOI: 10.3897/Nature Conservation.55.108688
Magazine information:
nature conservation
[ad_2]
Source link