[ad_1]
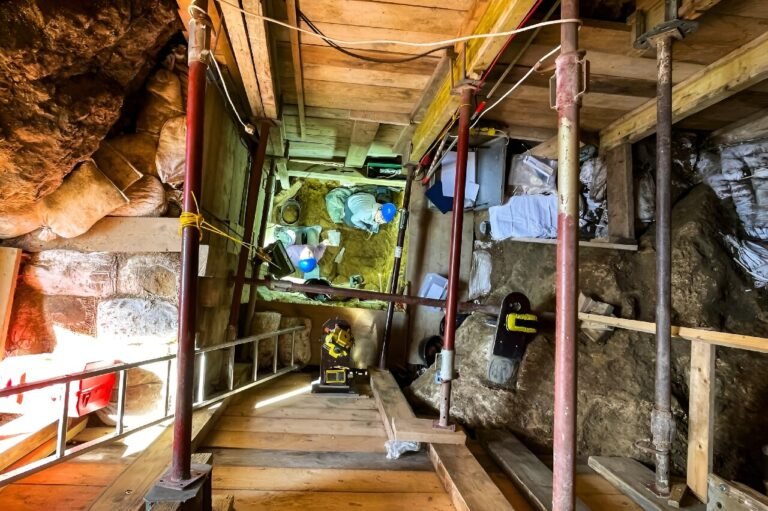
Researchers at the site in Ranis, Germany, had to avoid giant rocks to find man-made tools.
× close
Researchers at the site in Ranis, Germany, had to avoid giant rocks to find man-made tools.
A group of pioneering humans braved frigid conditions to settle in northern Europe more than 45,000 years ago, meaning they may have lived there alongside Neanderthals. It was a “big surprise,” scientists announced Wednesday.
An international team of researchers has discovered human bones and tools hidden behind a giant rock in a cave in Germany. This is the oldest trace of Homo sapiens ever discovered.
The discovery tells the story of how this species came to live in Europe and how it came to replace the Neanderthals, who mysteriously went extinct just a few thousand years after humans arrived. may be rewritten.
French paleoanthropologist Jean-Jacques Hublin, who led the new study, said there was a “replacement phenomenon” between the Middle and Upper Paleolithic periods, when the two coexisted in Europe. .
Archaeological evidence has been discovered, including stone tools of both types, dating back to this period, but the lack of bones makes it difficult to determine exactly who made what. There is.
Particularly puzzling are the tools of the so-called Rinkombi-Lannisian-Jerzmanowicyan (LRJ) culture, which have been discovered in several locations north of the Alps, including in Britain and Poland.
One such site, near the town of Ranis in central Germany, was the focus of three new studies published in the journal. Nature.
hide behind a rock
The cave was partially excavated in the 1930s, but the research team expected to find more clues during excavations from 2016 to 2022.
Excavations in the 1930s were unable to overcome the approximately 2-meter (6-foot) rock blocking the path. But this time, scientists were able to remove it by hand.
“We had to go 8 meters (26 feet) underground and put boards on the walls to protect the excavator,” said Hublin, from Germany’s Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology.
They were rewarded with leaf-shaped stone blades and thousands of bone fragments found at other LRJ sites.
The researchers used a new technique called paleoproteomics, which extracts proteins from fossils, to determine which bones were from animals and which were from humans.
Using radiocarbon dating and DNA analysis, they confirmed that the cave contained the skeletal remains of 13 humans.
The location of this cave is beneath Ranis Castle in central Germany.
× close
The location of this cave is beneath Ranis Castle in central Germany.
This means that the stone tools in the cave, once thought to have been made by Neanderthals, were actually made by humans 47,500 years ago.
Study co-author Marcel Weiss said: “Until now, no hominid remains have been known from LRJ, so this was a big surprise and shows that our hard work in the field has paid off.”
This fossil dates from when the first Homo sapiens left Africa for Europe and Asia.
“We’ve long thought about the great wave of Homo sapiens that swept across Europe toward the end of these transitional cultures about 40,000 years ago and rapidly absorbed Neanderthals,” Hublin said. he said.
But the latest findings suggest that humans settled on the continent earlier than previously thought, through repeated small-scale migrations.
cold change
This means that modern humans coexisted with their Neanderthal cousins for much longer, the last of which went extinct in southwestern Europe 40,000 years ago.
Researchers say this particular group arrived in northern Europe, which was much colder than today and resembled modern-day Siberia and northern Scandinavia.
They lived in small, nomadic groups, staying in caves for short periods of time, and ate the meat of reindeer, woolly rhinos, horses, and other animals they caught.
“How did people from Africa get the idea to go to these extreme temperatures?” Havlin said.
In any case, he added, humans have proven that they have the “technical capabilities and adaptability necessary to survive in harsh environments.”
It was previously thought that humans would not be able to withstand such cold temperatures until several thousand years later.
But humans lived longer than Neanderthals, who had long been accustomed to the cold.
What happened to Neanderthals remains a mystery. However, some blame humans for driving humans to extinction through violence, the spread of disease, or simply interbreeding with humans.
For more information:
Jean-Jacques Hublin: Homo sapiens reached the high latitudes of Europe by 45,000 years ago. Nature (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41586-023-06923-7. www.nature.com/articles/s41586-023-06923-7
Stable isotopes show that Homo sapiens dispersed across the cold steppe around 45,000 years ago in Ilsenhöhle, Ranis, Germany. Nature (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41559-023-02318-z, www.nature.com/articles/s41559-023-02318-z
Ecology, survival, and diet of Homo sapiens observed approximately 45,000 years ago at Ilsenhöhle, Ranis, Germany. natural ecology and evolution (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41559-023-02303-6, www.nature.com/articles/s41559-023-02303-6
Magazine information:
Nature
natural ecology and evolution
[ad_2]
Source link