[ad_1]
Editor’s Highlights are summaries of recent papers by AGU journal editors.
sauce: Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmosphere
Natural and anthropogenic atmospheric particles interact with solar radiation and play an important role in climate change, so a solid understanding of past changes in the composition and concentration of these particles in the atmosphere is important.
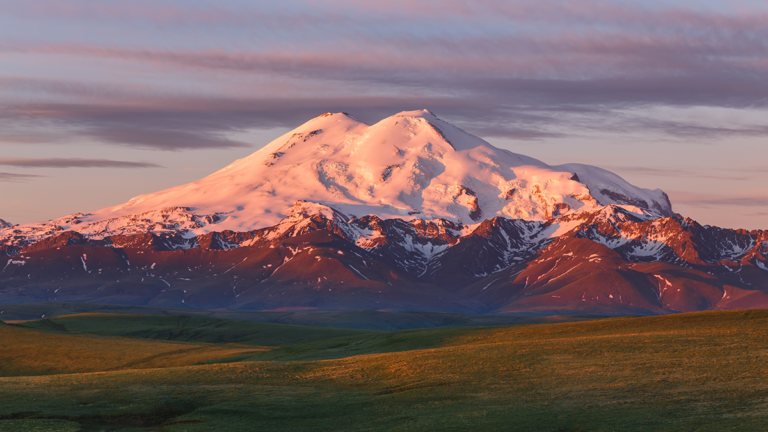
Organic carbon (OC) is the major component of modern aerosols, but its sources are less understood than other aerosols such as sulfate. Legrand et al. [2024] Investigating OC and its radiocarbon (14C) Using characteristics of ice cores from the Caucasus, we reconstruct and discuss past OC changes in southeastern Europe.
The authors found that despite increasing emissions from fossil fuel combustion, plant emissions of organic compounds remain the main source of particulate OC during summer in southeastern Europe. There is strong temporal variability in OC, which is due to changes in plant emissions in response to historical variations in summer temperatures in the region. The authors also found that since 1960, winter emissions from fossil fuels have become nearly as large as biogenic emissions, including wood burning, during that season.
Citation: Legrand, M., Preunkert, S., Kutuzov, S., Siour, G., Mikhalenko, V., Dolgova, E., & Friedrich, R. (2024). 20th century DOC changes and 14C signatures recorded in Caucasus ice cores: Implications for past sources of organic carbon aerosol in southeastern Europe. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmosphere129, e2023JD040121. https://doi.org/10.1029/2023JD040121
—Abdelwahid Mehrouki, Editor JGR: Atmosphere
Text © 2024. Author(s). CC BY-NC-ND 3.0
Unless otherwise noted, images are subject to copyright. Reuse of images is prohibited without the express permission of the copyright holder.
Related
[ad_2]
Source link