[ad_1]
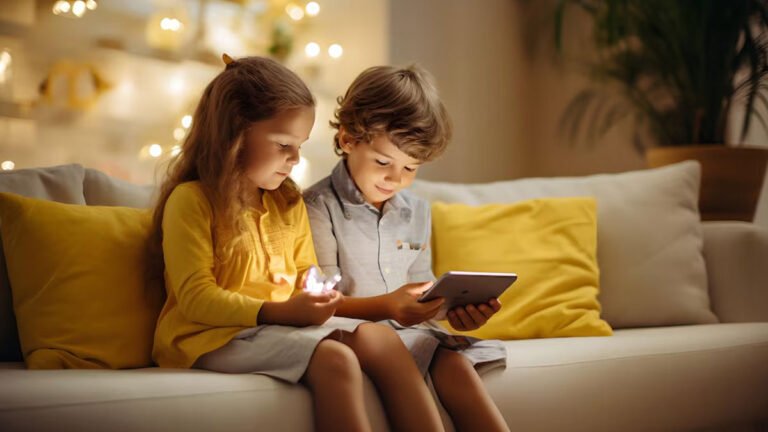
These days, eating healthy food, especially getting your kids to eat it, seems like an impossible dream. Junk food, processed food, sugary food, and fast food are frequently consumed by children, making them sick. Moreover, we rarely see kids playing on playgrounds. Instead, kids these days are glued to screens leading a sedentary lifestyle.
But this sedentary behavior can be harmful to children’s health: Recent studies have shown that children who are sedentary for more than six hours a day are at significantly higher risk of severe fatty liver disease and cirrhosis.
the study
A study published in the journal Nature’s Gut and Liver found that children who spend more than six hours a day sitting during their waking hours are at significantly increased risk of developing fatty liver disease and cirrhosis by young adulthood. According to study lead professor Andrew Agbaje, the findings suggest there is likely a causal relationship between sitting and liver damage.
Participants in the study, ages 17 to 24, underwent liver ultrasound to look for signs of liver scarring and fatty liver disease. On average, young participants spent six hours sitting or engaged in other sedentary activities per day, which increased to nine hours by the time they reached adulthood. By age 25, children had a 15% increased risk of developing fatty liver disease for every 30-minute increase in sedentary activity beyond six hours per day, according to the study.
To get a proper explanation of the relationship between sedentary behavior and fatty liver in children, OnlyMyHealth Dr R Kishore Kumar, Neonatologist and Paediatrician, Cloud9 Group of Hospitals, Bangalore.
Also read: Does fatty liver disease increase your risk of heart disease? Read what the experts say
Sedentary lifestyle and liver problems
According to Dr Kumar, a sedentary lifestyle is a habit and not a genetic one. “The excess calories that you do not consume start being stored in the body in the form of fat so that you can utilise them in future. Depending on the amount stored, fat gets stored in different parts of the body.” This stored fat can lead to NAFLD (Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease), which means excess fat accumulates in the liver.
Commenting on the findings, Dr Kumar said: “This emerging health issue, which is mostly associated with adults, is now seeping into the younger generation as well due to changing lifestyles,” adding: “We have long known that physical inactivity is a risk factor for various health problems, including obesity and cardiovascular disease. However, the direct link with fatty liver disease in children highlights the urgent need to address sedentary behaviour at an early stage.”
A sedentary lifestyle and its consequences
In today’s digital age, children are spending more time in sedentary activities like watching TV, playing video games and using computers and tablets. Dr Kumar says, “The shift from active play to screen-based entertainment has serious health implications. Children are naturally active – they run, play and explore – but our modern environment discourages these natural behaviours. Sitting for long periods of time can lead to metabolic changes and accumulation of fat in the liver.”
Talking about how a sedentary lifestyle impacts fatty liver, Dr Kumar explains: “The metabolic effects of a sedentary lifestyle include decreased insulin sensitivity, increased adiposity and altered lipid metabolism. These factors combine to contribute to the development of NAFLD.”
Also read: Why is fatty liver so prevalent among young people in India? Experts explain
Precautions
Preventing NAFLD in children requires a multifaceted approach focusing on promoting physical activity, improving dietary habits, and reducing sedentary time.
1. Encourage physical activity
According to Dr. Kumar, children should get at least 60 minutes of moderate to vigorous exercise every day. This could include activities like biking, swimming, playing sports, active play at home or in the park, or even walking up and down the stairs in the building where they live instead of using the elevator frequently.
2. Improve your eating habits
A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains and lean proteins is essential. Reducing the intake of sugary drinks, fast food and high-fat snacks can significantly reduce the risk of developing NAFLD. Dr Kumar advised that parents should focus on preparing home-cooked meals and involving their children in the cooking process to inculcate healthy eating habits.
3. Reduce Screen Time
Dr Kumar, who recommends limiting screen time, says, “Limiting screen time to less than two hours a day can reduce the risks associated with a sedentary lifestyle. Encouraging alternative activities like reading, hobbies and outdoor play can also be effective.”
Finally, he said, “Parents and caregivers need to be proactive and create balanced habits that naturally incorporate physical activity into their children’s daily lives.”
[ad_2]
Source link