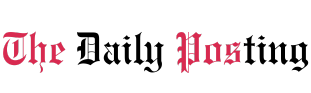[ad_1]
We now have a better idea of where the European Space Agency is. Rosalind Franklin ExoMars spacecraft I’ll drive when I land Mars Our mission to search for life is all thanks to a brand new geological map of the landing zone.
“This map is exciting because it’s a guide to where the answers are,” said Peter Faudon of the Open University. press statement. “This serves as a visual hypothesis for what we currently know about the different rocks at the landing site. Rosalind Franklin’s instruments will allow us to test our knowledge on the fly when we need to. ”
Originally a partnership with Russia, which provided the spacecraft’s landing platform, the mission I’m late Scientists are reviewing the mission and designing and building a new landing platform with the aim of reaching Mars by 2030, with a new launch date expected by October 2028.
Related: ExoMars: European astrobiology mission to Mars
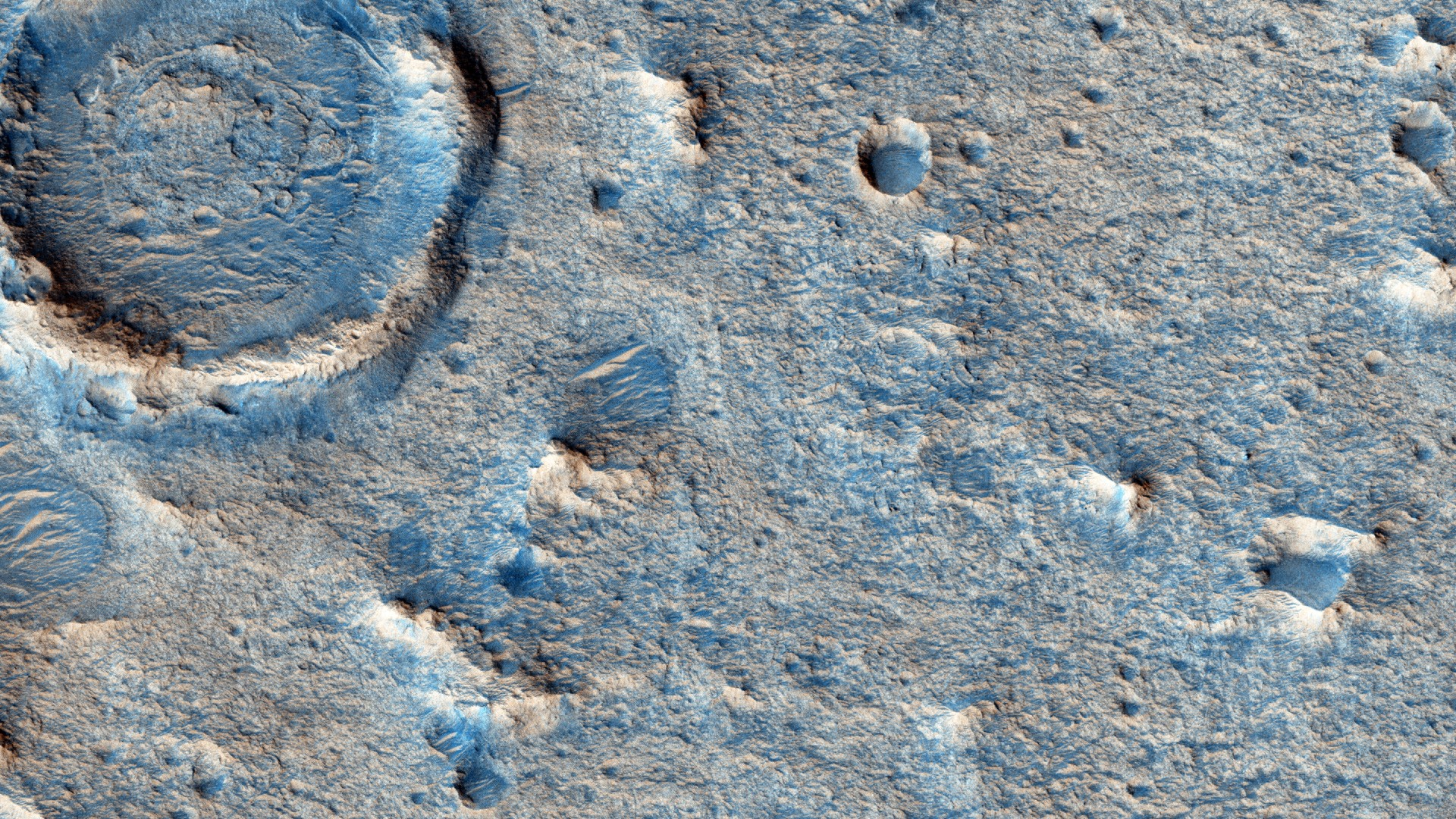

Given Mars’ cold, dry, and irradiated conditions, it is highly unlikely that we will find microbes living on Mars today, but a common hypothesis is that Mars is warm, wet, and home to 3.5 billion It is possible that there was an environment that could support life more than a year ago. I’ve seen the evidence For this, in the ruins of river channelfloodplains and coasts, the mineralogy of these areas, and presence of organic molecules.
If life existed in the distant past, its biological signatures likely remain locked away in Martian rocks, awaiting discovery by the Rosalind Franklin spacecraft.
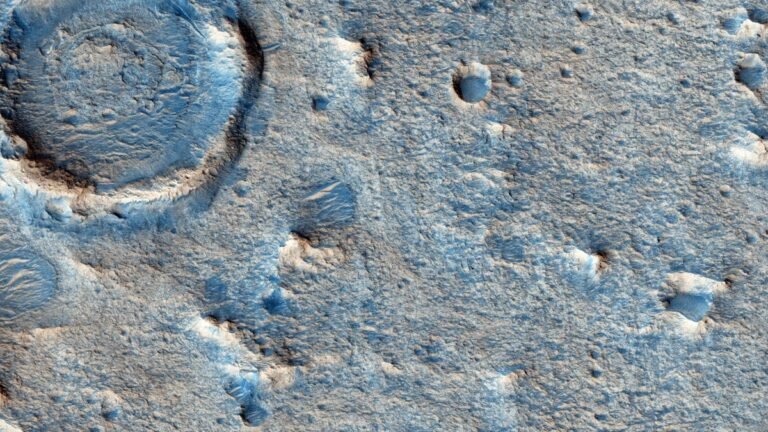
The rover’s mission will include traversing many kilometers across the Oxian Planum, a vast plain rich in minerals, including clay, deposited by liquid water in ancient times. The rover will periodically drill 2 meters (6.5 feet) into these clay deposits and retrieve samples for analysis with the rover’s suite of Pasteur instruments.
Clay is considered an excellent material for preserving biosignatures, and the Mars Organic Molecular Analyzer (MOMA) will be among the tools the rover will use to study these samples. MOMA will test sampled materials to try to identify organic carbon-based molecules. Things like amino acids, lipids, and even RNA and DNA (or Martian analogues) that could only be left behind by life.Therefore, why did the rover do this? named after Rosalind Franklina British chemist who played a key role in understanding the structure of DNA.
But once the rover’s wheels touch Martian soil, the scientists return to the rover’s wheels. earth You need to know where to drive Rosalind Franklin to give you the best chance of achieving your goals.
Therefore, the new map includes boulder fields, wind horizontal ridge (TAR) is characterized by wind, associated materials such as widely spaced fractures, craters, and ejecta, honeycomb material formed from polygonal and straight valleys, overlying dark material, and various rock types. It is thought to have been formed by layers of sediment that are almost 4 billion years old. .
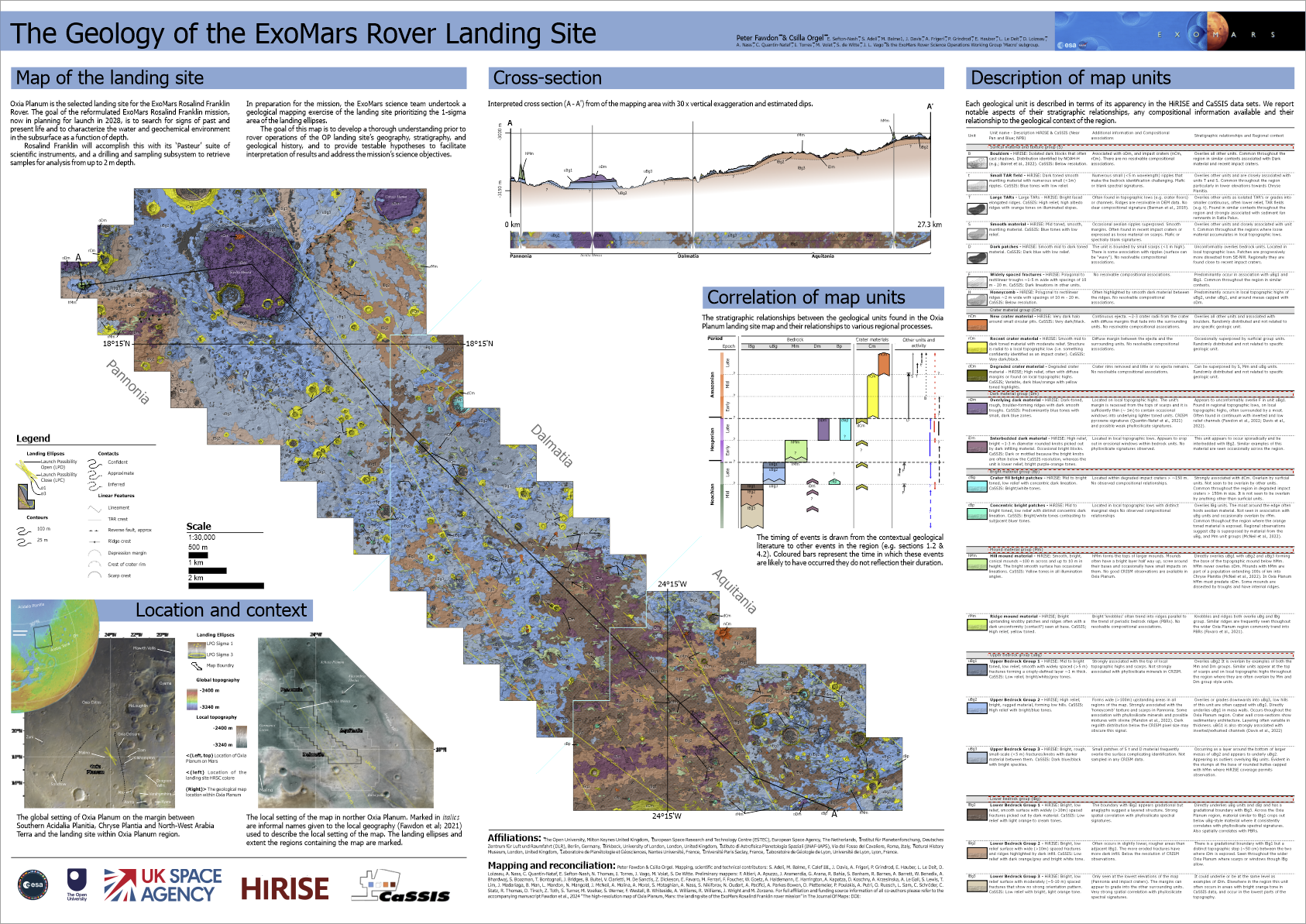
It is still not clear how all these features were formed. Polygonal shapes are often associated with subsurface ice and permafrost that are typically found at high latitudes, for example, but the presence of subsurface ice on the Oxian Planum, at latitudes as low as 18 degrees north of the Martian equator, is still unknown. It has not been discovered (although Ice discovered elsewhere near Mars’ equator).
These different geological types and the periods in which they originated: the Noachian period from 4.1 billion to 3.7 billion years ago, the Hesperian period from 3.7 billion to 3 billion years ago, and the Amazonian period from 3 billion years ago to the present. ) are color-coded. – Coded on the map. The scale is 1:25000, meaning that 1 centimeter (0.4 inch) on the map represents 250 meters (820 feet) on Mars. The rover travels an average of 25 to 50 meters (82 to 164 feet) per day, making up only a few millimeters on the map.
The origin of this map is actually a COVID-19 lockdown project, in which 80 trained volunteers used data from Europe’s ExoMars Trace Gas Orbiter and NASA to find 134 gases per square kilometer. Characterized individual locations. mars reconnaissance orbiter.
The rover’s lead scientist then pieced together all the information from the volunteers to create the final version of the map, which map journal.
[ad_2]
Source link